⭐⭐ CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE⭐⭐
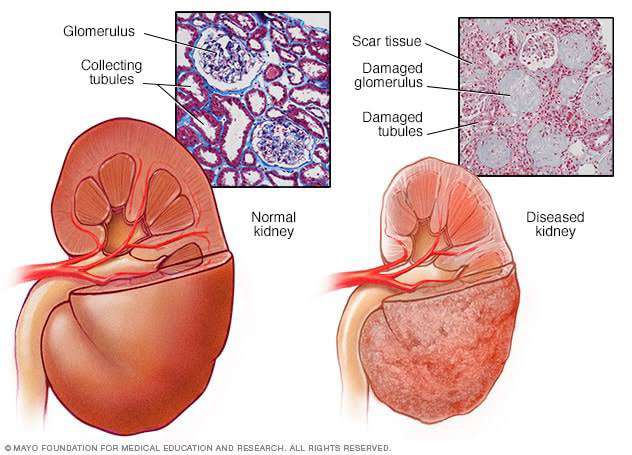
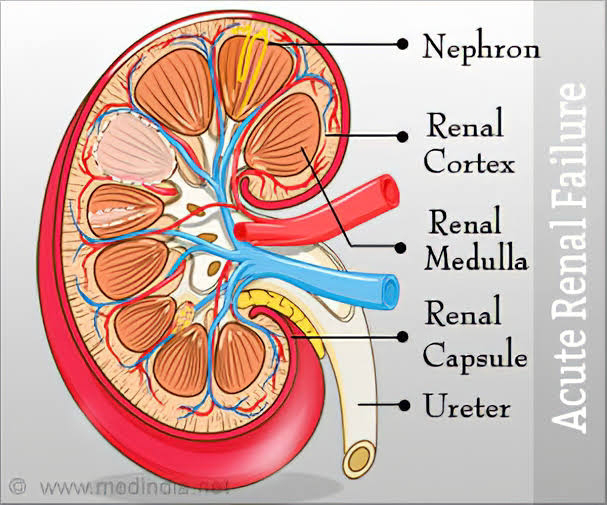
⭐⭐ CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE ⭐⭐ ( CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE ) ( END STAGE KIDNEY DISEASE ) 1) DEFINITION OF CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE ( CRF ) :- CRF is chronic and irreversible deterioration of kidney function for atleast > 3 months with GFR < 15 ml/ min/ 1.73 sq metres of body surface area. 2) CAUSES OF CRF :- (I) Glomerulonephritis :- It is the inflammation of glomeruli. GN occurs due to various causes like - post streptococcal GN, - As a part of autoimmune diseases like SLE, Wegener's granulomatosis ,etc - Due to primary glomerular disease like cresentic GN, membranous GN, Diffuse proliferative GN. GN occurs due to deposition of circulating immune complexes or deposition of antibodies due to above causes which may act against antigens in glomerular basement membrane ( molecular mimicry) (II) Chronic pyelonephritis ( reflux nephropathy ) :- - Normally during micturition, urine doesn't go back into the ureters f