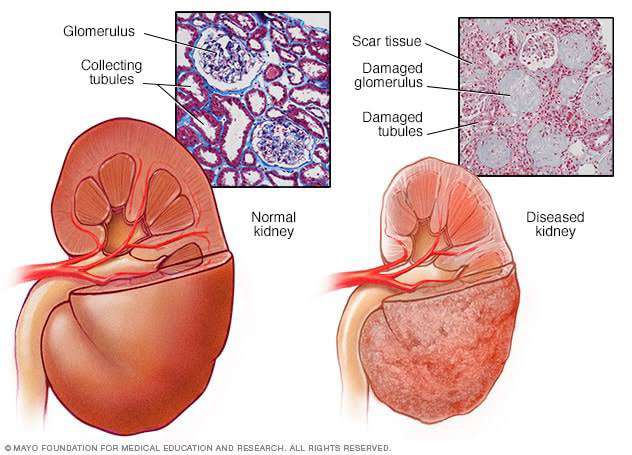
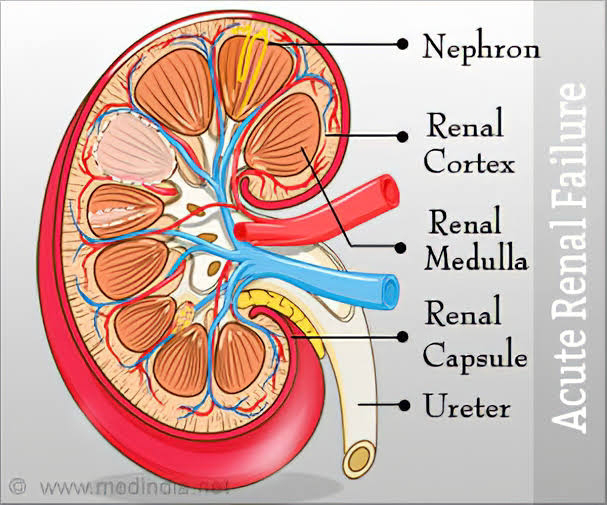
⭐⭐⭐ KIDNEY STONES ⭐⭐⭐
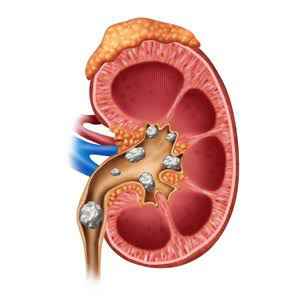
⭐⭐⭐ KIDNEY STONES ⭐⭐⭐ 1) DEFINITION OF KIDNEY STONES:- Kidney stones are hard, pebble-like pieces of material that form in one or both of your kidneys . 2) CAUSES OF KIDNEY STONES :- (I) Hyperparathyroidism :- i.e increased production of parathyroid hormone. - Hyperparathyroidism leads to hypercalcaemia i.e increased levels of calcium in the blood. This extra Calcium enters the kidney for excretion. Thus, increased concentration of calcium in kidney leads to formation of kidney stones. - Hyperparathyroidism causes hypercalcaemia because PTH hormone causes increased renal resorption of calcium, increased synthesis of active form of vitamin D (which increases intestinal calcium absorption), and increased resorption of the bone. - Following conditions can cause hyperparathyroidism :- # Noncancerous growth or cancerous growth or hyperplasia of parathyroid gland. # Severe calcium deficiency - low blood calcium stimulates parathyr