⭐⭐ HYPERTENSION ⭐⭐
⭐⭐ HYPERTENSION ⭐⭐
1) DEFINITION OF HYPERTENSION :-
Blood pressure that is higher than normal is known as Hypertension.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
2) CRITERIA OF HYPERTENSION :-
(a) Above 60 years - There is
hypertension if
Systolic BP > 150 mm Hg
Diastolic BP > 90 mm Hg
(b) Below 60 years - There is
hypertension if
Systolic BP > 140 mm Hg
Diastolic BP > 90 mm Hg
(c) Above 18 years with diabetes or
Chronic Kidney Disease - There is
hypertension if
Systolic BP > 140 mm Hg
Diastolic BP > 90 mm Hg
⭐ White coat hypertension - BP rises in
hospital. Take readings at home. (Occurs due to anxiety & increased sympathetic response in hospital)
⭐ Isolated ambulatory or masked hypertension - BP is normal at hospital but more at home. Such patients have risk of organ damage.
⭐ Paradoxical hypertension - Paradoxical rise of BP in patients taking antihypertensive drugs.
In patients with diabetes & hypertension taking Beta blockers, if there is hypoglycemia (due to inhibition of hepatic glucose production by Beta blockers) - Sympathetic response is produced to increase blood glucose & hence BP increases.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
3) CLASSIFICATION OF HYPERTENSION -
(a) Primary or Essential hypertension -
# In most of the cases.
# No specific cause.
# 70 % cases have family history.
(b) Secondary hypertension -
# Less number of cases.
# Caused due to a disease.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
4) CAUSES OF HYPERTENSION -
(a) Pre eclampsia - in pregnancy
(b) Coarctation of aorta - There is
narrowing of aorta which may be due to
abnormalities during development or
genetic cause. This narrowing causes increase in BP.
(c) Renal diseases -
# Chronic pyelonephritis.
# Glomerulonephritis.
# Polycystic Kidney Disease.
# Renal artery Stenosis.
When kidneys receive less blood flow
(as in case of renal artery stenosis or
due to damage to renal vessels in renal Infection)
they release Angiotensin which leads
to increase in BP.
Also, the kidney damage impairs the
kidney's ability to filter fluid from the
blood leading to increase in fluid
volume in the blood, thus causing
increase in BP.
(d) Endocrine diseases -
(I) Cushing's syndrome - Increased
Aldosterone (mineralocorticoid) which causes sodium retention & increased BP
(II) Pheochromocytoma - There is
increased Adrenaline production which
leads to increased BP
(III) Adrenal hyperplasia - Increased
secretion of Aldosterone &
catecholamines.
(IV) Hyperthyroidism -
Other features - diarrhoea, weight loss,
exophthalmos, increased heart rate,
heat intolerance, etc.
(V) Hyperparathyroidism - Increased
parathyroid hormones cause increase in blood calcium level which increases activity of Renin Angiotensin
Aldosterone System causing rise in BP.
(e) Alcohol & drugs -
# OC pills.
# Cyclosporine.
# Sympathomimetics.
# Corticosteroids.
Ask history of this drugs.
(f) Obstructive sleep apnea - Breathing
stops during sleep for sometime.
Sudden drop in oxygen causes RAAS
activation & increase in BP.
Causes -
# Obesity - Excess soft tissue in mouth
& throat is relaxed during sleep. It can
cause blocking of airway.
# Enlarged tonsils.
# Tumor in airway.
# Down's syndrome.
# Thick neck.
# Smoking, alcohol & sedatives.
⭐⭐⭐⭐
⭐ Causes of isolated systolic hypertension ⭐:-
(a) Atherosclerosis - cholesterol plaque
causes obstruction to blood flow
leading to increased blood pressure.
# Investigations - lipid profile
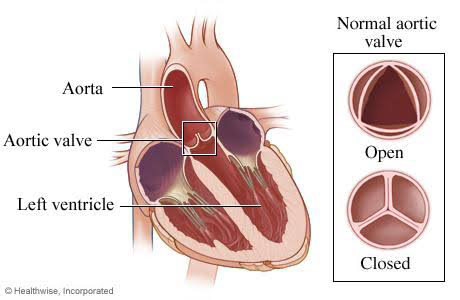
(b) Aortic regurgitation -
Due to regurgitation, end diastolic
volume of left ventricle increases
which leads to dilatation of left
ventricle and increased stroke volume
( Frank starling law) - increased BP
(c) Coarctation of aorta - explained
above.
(d) Hyperthyroidism - explained above
(e) Patent ductus arteriosus -
Normally ductus arteriosus is the
communication between pulmonary
artery and aorta before birth. Blood
goes from pulmonary artery to aorta
thus bypassing the non working fetal
lungs.
Persistence of ductus arteriosus after
birth is called patent ductus arteriosus.
Too much blood circulating through
heart's main arteries through PDA can
lead to pulmonary hypertension.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
5) MEASUREMENT of BP -
# 2 readings per day for 3 days.
One reading in sitting or supine position
& other in standing position. Reading in
standing position is taken to check for
postural hypertension.
# Person should be seated in chair with
back resting & arm at heart level. No
consumption of tobacco or caffeine 30
to 45 minutes before checking BP.
# Reading on both arms are taken. One
which is high is taken. If difference is
more than 10 mm Hg, there may be obstructive lesion of aorta, subclavian artery.
# When the sound of beat is heard
(phase I of Korotkoff sound) systolic BP
is obtained & when sound stops (phase
V) diastolic BP is obtained. # Auscultatory gap -Sound starts, then
disappears in middle, then again starts
& finally disappears. It is seen in some
hypertension patients. There may be
misreading i.e high diastolic BP or low
Systolic BP depending on the phase
heard. To avoid this, palpatory method
should be done prior to auscultatory
method.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
6) CLINICAL FEATURES RELATED TO
HYPERTENSION :-
(a) Risk factors of Hypertension:-
# Obesity - atherosclerosis
# Hyperlipidemia - causes
atherosclerosis . Check lipid profile
# smoking - harmful byproducts
cause damage to vessel leading to
hypertension
# sedentary lifestyle
# Diabetes - Diabetes may decrease
the production of nitric oxide
( Vasodilator) thus leading to
vasoconstriction and raised BP
# Positive family history
(b) Clinical features due to hypertension
itself:-
(I) Mostly asymptomatic - found on
examination.
(II) Acute hypertension -
# Transient headache - increased
pressure in brain vessels can cause
fluid to leak out causing swelling of
brain. This swelling leads to
pressure on brain and headache.
# polyuria - Nocturnal polyuria .
At daytime , blood flow to kidney
decreases due to vasoconstriction.
At night, levels of dopamine and
noradrenaline are lower. This causes
vasodilation and increased renal
blood flow - polyuria.
(III) Chronic hypertension :-
Left ventricular hypertrophy - due to
increased workload on left ventricle
to pump against the systemic
resistance.
Heaving apical impulse
(IV) Enlarged left atrium ( due to
backpressure on left ventricle and
atrium because of systemic arterial
resistance ) and 4th heart sound
( due to left ventricular hypertrophy)
(V) Accentuation ( louder) of aortic
component of 2nd heart sound -
forceful shutting of aortic valve at
the end of ventricular systole due to
pumping against systemic
resistance.
(VI) Very short early diastolic murmur
(c) Clinical features due to diseases
causing hypertension :-
(I) Coarctation of aorta -
Other symptoms -
# Absent leg pulses.
# Difference in BP between arms & legs i.e. high BP in arms & low BP in legs.(narrowing of aorta in coarctation is usually located after arteries branch to the upper body. Thus , Coarctation can lead to high
BP and pulsing of blood in head and
arms and low BP and weak pulses in
in legs and lower body)
# Systolic murmur (due to narrowed aorta) below scapula.
# Bounding pulse in arms, carotid.
# Collaterals around scapula ( due to
increased BP)
# systolic murmur over spine
(II) Renal diseases :-
In case of renal cause of hypertension, following symptoms may accompany
raised BP -
# Dysuria i.e. burning micturition.
# Hematuria.
# Edema (due to extra fluid and
sodium in circulation when Kidney is
unable to filter them)
# Loin pain.
# Oliguria
# UTI.
# Enlarged kidney - in Polycystic
Kidney disease.
# Bruit over lumbar region - renal
artery stenosis
# Fever, backache and recurrent UTI -
chronic pyelonephritis
(III) Endocrine diseases :-
# Cushing's syndrome- increased
levels of glucocorticoid ,
mineralocorticoid, androgens.
Other features - central obesity,
moon face, hump, stretch marks,
purple striae,etc.
# Pheochromocytoma -
Other features - Palpitations,
headache, panic attacks due to
increased catecholamines.
# Adrenal hyperplasia -
Other features - Features of Cushing's syndrome, palpitations, panic attacks. Masculine features due to increased androgens such as increased facial & body hair, irregular menstrual periods, etc.
# Hyperthyroidism -
Other features - diarrhoea, weight loss, exophthalmos, increased heart rate, heat intolerance, etc.
(IV) Alcohol and drug intake:-
Ask history for these
(V) Obstructive sleep apnea -
Breathing difficulty during sleep
(VI) Atherosclerosis -
# Other features - There may be pain in leg on exercising, features of stroke, etc.
(VII) Aortic regurgitation -
# Other symptoms -
Palpitations - due to regurgitation,
end diastolic volume of left
ventricle increases and hence
stroke volume increases due to
more stretching of ventricle
( Frank starling law)
Pulsations in neck
Angina - muscle fatigue
Dyspnea - after ventricular failure
Syncope
Signs like - Water hammer pulse,
Rosenbach sign, Gerhard sign ,etc
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
7) COMPLICATIONS OF HYPERTENSION :-
(a) Cardiovascular complications :-
Occurs due to damage to the vessels
and chambers of heart because of
high blood pressure.
(I) Coronary artery Disease
(II) Aortic dissection - tear in the inner
layer of aorta.
(III) Aortic aneurysm - abnormal bulge
or enlargement.
(IV) Left ventricular failure - as it has
to pump against the systemic
vascular resistance.
(b) Renal complications :-
It occurs due because high blood
pressure causes arteries around the
kidney to narrow, weaken or harden.
These damaged arteries are not able
to deliver enough blood to the kidney.
Hypertension also causes damage to
glomeruli due to high blood pressure
and impairs the ability of filtration.
(I) Proteinuria
(II) Progressive renal failure
(c) Malignant hypertension :-
Severe rise in BP, retinal haemorrhage
and exudates ( due to leakage) , visual disturbances, headache (explained above) , vomiting ,renal damage.
(d) CNS Complications :-
(I) Cerebral haemorrhage due to
vessel damage.
(II) Subarachnoid haemorrhage
(III) Transient ischaemic attack due to
intracranial atherosclerosis
(IV) Hypertensive encephalopathy
(e) Ophthalmic complications :-
due to damage to the vessels in retina
(I) Grade I = Retinal arteriole
thickening and increase in light reflex over arterioles.
(II) Grade II = Retinal arteriole
thickening and arteriovenous nipping
(III) Grade III = Grade II + flame
shaped haemorrhages and soft
exudates.
(IV) Grade IV = Grade III +
papilloedema.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
8) INVESTIGATIONS OF HYPERTENSION:-
(a) Basic investigations :-
(I) Blood urea and serum creatinine -
tell about renal function.
(II) Urine test for sugar , blood, protein
and microscopy - Tell about Urinary
tract infection and renal function
(III) Fasting and postprandial blood
sugar - Diabetes mellitus
(IV) Chest X ray - enlarged heart,
dilated vessels
(V) ECG - left ventricular dysfunction
(VI) Serum calcium and uric acid
(VII) Blood cholesterol and
triglycerides - atherosclerosis
(VIII) Serum electrolytes -
hyperaldosteronism ( sodium
retention) , hyperparathyroidism
( increased blood calcium) etc.
(b) Investigations related to causes :-
(I) Coarctation of aorta
Investigations - Chest X ray
Echocardiogram
Catheterization
(II) Renal diseases -
Following investigations can be carried out -
# Renal function tests.
# Urine examination.
# USG.
# CT
# IVU - Polycystic kidney
(III) Endocrine diseases -
# Cushing's syndrome-
Investigations - Urine & blood tests
of hormone levels, saliva test.
# Pheochromocytoma -
Investigations - Plasma Metanephrine testing , 24 hour urinary collection of
catecholamines.
# Adrenal hyperplasia -
Investigations - Blood & urine tests for hormones.
# Hyperthyroidism -
Investigations - serum T3 ,T5 , TSH
# Hyperparathyroidism
Investigations - Serum Calcium level, level of parathyroid hormones in blood,
phosphorus levels, CT, USG, etc.
# Acromegaly - GH levels and
radiography of skull.
# Hyperaldosteronism - Elevated
aldosterone levels , hypokalemia
( Aldosterone causes sodium
retention and thus increases BP)
(IV) Aortic regurgitation :-
Investigations :-
Auscultation
Echocardiography
Coronary angiography
ECG
Chest Xray
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
9) TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION :-
(a) General measures :-
(I) Avoid smoking and alcohol - These
cause damage to the blood vessels
and plaque formation.
(II) Low salt intake - Sodium causes
BP to raise.
(III) Low intake of saturated fats - fats
promote atherosclerosis
(IV) Exercise - Exercise increases the
capacity of heart. Stronger heart
can pump more blood with less
effort . Hence, force on the arteries
decreases due to which BP
decreases
(V) Relaxation and meditation -
Stress causes sympathetic fight &
flight response which causes
release of hormones like
adrenaline due to which
vasoconstriction occurs ,heart rate
increases and BP increases.
(VI) Include vegetables and fruits in
diet - vegetables are rich in nitrates
(Vasodilator)
(b) Antihypertensive drugs :-
(I) Diuretics -
# Thiazides - They influence carbonic anhydrase and prevent
reabsorption of sodium bicarbonate
at PCT and Na+ & Cl- at DCT.
Drugs - Chlorothiazide
Hydrochlorothiazide
(Preferable in older
individuals)
# Loop diuretics - Used when more
sodium excretion is required.
Potassium loss occurs due to
reduced H+ secretion.
Drugs - Furosemide, Torasemide.
# Potassium sparing diuretics -
Amiloride.
# Aldosterone antagonist -
Spironolactone.
(II) Beta blockers -
MOA - sympatholytic, deceases
heart rate & BP.
Contraindications - Asthma
COPD
Diabetes
Heart block
Cardioselective Beta 1 blockers-
Atenolol, Metoprolol - Can be used
in asthma, COPD.
(III) alpha + beta blockers -
Labetalol, Carvedilol.
(IV) ACE inhibitors -
MOA - They inhibit ACE. Therefore,
no formation of Angiotensin II
leading to vasodilation. There is no
release of aldosterone.
Drugs - Captopril, Lisinopril, Enalapril.
(V) Angiotensin Receptor Blockers -
MOA - They block 81 receptors.
Therefore, no action of Angiotensin II.
Drugs - Losartan, Candesartan.
(VI) Direct Renin inhibitors-
MOA - No activation of RAAS.
Drugs - Alliskiren.
(VII) Calcium Channel Blockers -
MOA - Blockage of calcium channels
inhibits cardiac muscle contraction.
Negative inotropic effect.
Drugs - Verapamil, Diltiazem,
Nifedipine, Amlodipine.
(VIII) Vasodilators -
Drugs - Hydralazine, Minoxidil.
(IX) Alpha blockers -
Drugs - Prazosin.
(X) Alpha 2 blockers -
Drugs - Clonidine.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐


Writing skills are top class
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
Deleteखूप सुंदर लिखाण
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteNice presentation
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
Deleteबढ़िया👌
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteNice nice nice
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteThank you so much 😊😊
ReplyDeleteGood
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteBrilliant wriitiing
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
Delete👌👌👌
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
Delete👍👍
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteBeauty
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
Delete👌👌👌👌👌
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteThank you so much 😊😊
ReplyDeleteWell done
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
ReplyDeleteBahut Khoob
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteThank you so much 😊😊
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
ReplyDeleteNice
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
Delete