⭐⭐GALL STONES ⭐⭐
⭐⭐GALL STONES ⭐⭐
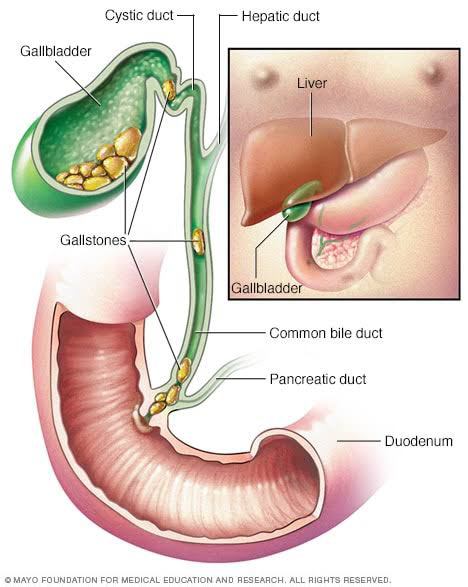
Gall stones are solid crystal deposits formed in the gall bladder, a pearly shaped sac that stores bile.
2) TYPES of Gall stones :-
(I) Cholesterol stones
(II) Mixed stones - Made of cholesterol ,
calcium salts of carbonate,
phosphate, palmitate , proteins.
(III) Pigment stones - black or greenish
black coloured.
⭐ NOTE ⭐-
# Sources of cholesterol in our body
are liver and food. Liver produces
cholesterol.
# Cholesterol in liver helps in production
of bile acids (cholic ,chenodeoxycholic
acids,etc) by classic and alternate
pathway.
# These bile acids further combine with
Glycine or taurine to form bile salts.
# Thus, bile juice contains bile salts ,
bile acids, phospholipids, cholesterol,
conjugated bilirubin, electrolytes ,
water.
# This bile juice is released into
intestine(duodenum) from gall bladder
Most of the bile salts and acids are
reabsorbed back into portal circulation
and reach back to liver - enterohepatic
recirculation.
( portal circulation consists of vessels
which carry blood from intestine to
the liver )
# Hepatocytes take up these bile acids
and salts from the portal venules and
again actively secrete them into bile
ductules.
# If this enterohepatic circulation is
impaired by one way or the other,
these bile acids will not be reabsorbed
from the intestine (ileum) and hence,
most of them will be excreted.
3) PATHOGENESIS of Gall stones:-
(a) Admiron's hypothesis -
# Cholesterol, which is secreted in
bile , is insoluble in water.
It is made soluble by micelle
formation with bile salts and lecithin.
# The normal bile salt : cholesterol
ratio is about 25 : 1.
If it goes below 13 : 1, relative
concentration of cholesterol
increases and precipitation of
cholesterol occurs - cholesterol
monohydrate crystal formation.
( One of the cause for decreased
bile salt concentration may be
defective enterohepatic circulation
as discussed above due to which bile
salts will not be reabsorbed and
concentration of bile salts will be
decreased leading to precipitation of
cholesterol crystals.
(b) Some cholesterol is present in
bilayered lipid vesicles. A specific
glycoprotein in bile causes
aggregation of these vesicles -
nucleation. This leads to formation of
cholesterol crystals due to nucleation.
(c) Pigment stones may be formed due
to increased bilirubin.
4) ETIOLOGY of Gall stones :-
(a) Infections - E coli, Salmonella,ascaris
chlonorchis sinensis ,etc.
(These infections cause damage to
intestinal wall which can impair
the function of absorption and thus
impair the enterohepatic circulation)
(b) Pancreatic juice reflux into bile duct
(Phospholipase present in pancreatic
juice converts lecithin to lysolecithin.
As lecithin is important for micelle
formation with cholesterol,
decreased lecithin leads to
precipitation of cholesterol.)
(c) Bile stasis - (Due to stasis,
supersaturation of bile occurs. This
promotes nucleation of cholesterol
crystals.)
Eg - # TPN i.e total parentral nutrition.
(Due to parentral nutrition - no
food to digest in intestine - no
secretion of bile in intestine -
stasis of bile.)
# patient on iv fluids
# pregnancy (progesterone impair
emptying of Gall bladder due to
effect on sphincter of oddi)
# vagotomy (decreased motility of
gall bladder - stasis
(d) Impaired enterohepatic circulation
(e) Factors increasing cholesterol -
# old age
# obesity
# oc pills
# clofibrate
(f) Factors decreasing bile acids and
lecithin -
# ileal resection - decreased
absorption of bile acids
# cholestyramine - It binds to bile
acids in intestine and causes it's
excretion
# estrogen - it decreases bile acid
transportation from hepatocytes
into bile canaliculi by inhibiting the
export pumps
(g) Pigment stones - due to increased
bilirubin. Increased bilirubin occurs in
case of hemolysis
- Hemolytic anemia
- Sickle cell anemia
- Hereditary spherocytosis
- Thalassemia
5) CLINICAL EFFECTS of Gall stones -
(A) On gall bladder :-
(I) May be asymptomatic
(II) Biliary colic - severe spasmodic
episode of pain in right
hypochondrium and epigastrium
which radiates to chest, upper
back, shoulder.
( Possible causes of pain -
# gall stones irritate mucosa and
nerve endings in the wall of
biliary apparatus .
# when the stone causes
obstruction ,bile stasis occurs.
This leads to spasm to gall
bladder in attempt of emptying.
This muscle spasm causes pain)
This type of pain is commonly
seen after fatty meals ( due to
increased contraction of Gall
bladder)
(III) Cholecystitis - Acute or chronic
( Due to obstruction and stasis of
bile - inflammation)
(IV) Empyema of Gall bladder - (pus
formed due to stasis - infection -
inflammation)
(V) Mucocele Gall bladder - Due to
outlet obstruction of Gall bladder
by stone.
(VI) Limey Gall bladder - high calcium
carbonate content - toothpaste
like material.
(VII) Carcinoma Gall bladder - due to
bile stasis and inflammation
(VIII) Perforation of Gall bladder-
Leads to biliary peritonitis and
pericholecystic abscess.
(B)On common bile duct (CBD) :-
(I) Cholangitis
(II) Pancreatitis
(III) secondary stones in CBD
(IV) Mirizzi syndrome - compression
of CBD by stone.
(C) On intestine :-
(I) Intestinal obstruction
(II) Gall stone ileus - obstruction -
spasm - pain.
6) Gall stone colic - It occurs due to spasm
of wall of Gall bladder due to impaction
of stone in cystic duct. It commonly
occurs in supine position, lasts for a
period of time, may be associated with
tachycardia, restlessness. It can cause
vomiting , Cholecystitis , Empyema GB.
7) INVESTIGATIONS for gall stones -
(a) USG abdo
(b) Xray
(c) CT
(d) LFT
(e) WBC count
8) TREATMENT of Gall stones:-
(I) Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
(Removal of Gall bladder)
(II) Laparotomy - through right subcostal
incision ( kochers incision)
Indications - carcinoma GB
CBD stones
patient unfit for
laparoscopy.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐


Perfect 👌👌👌
ReplyDeleteDr. Vinayak Patil
ReplyDeleteVery simple language, Not only doctor but every person can understood your artical.
Thank you so much 😊😊
DeleteDetailed explanation in very easy language.Wow!
ReplyDeleteLove from Bahamas ma'am😊
Thank you so much 😊😊
DeleteCool✨
ReplyDeleteखुप सुंदर लिखाण बेटा. पार्किंसन नंतर हा लेख खूप आवडला.
ReplyDeleteशैलजा सातपुते, वाशिम.
Thank you so much madam😊😊
DeleteBrilliantly written & presented !
ReplyDeleteDr.Joseph, Ukraine
Thank you so much sir for reading 😊😊
DeleteWriting skills💥✨
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteIndians always teach us alot. Doing well dear.
ReplyDeleteDr Beaven Frank, USSR
Thank you so much sir😊😊
DeleteI m a medical student from Pretoria & Never found such an easy explanation of formation of gall stones from cholesterol!
ReplyDeleteThank u so much Dr Nikita ma'am.😊
Thank you so much 😊😊 for reading
DeleteNicely presented work👍
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
DeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteFormation of gall stones explanation is lit💥
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
Deleteकाफी सुंदर प्रस्तुतिकरण👌
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteBeautiful
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteVery nice work
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteAll articles are very nice👍
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteVery good
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
Delete👌👌👌
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteAmazing
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteVery nice writing
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteEast or west, Dr Nikata is best😊
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteKeep writing dear
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteWomen power👌👌 U have power to do anything! Write anything so beautifully
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteGood
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteNice
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteThank you so much 😊😊
ReplyDelete👌👌
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteGallstone formation explanation was lit💥
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteThank you so much 😊😊
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
ReplyDelete