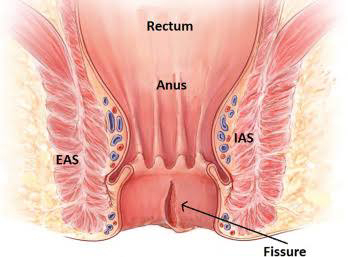
⭐⭐ ANAL FISSURE ⭐⭐
⭐⭐ ANAL FISSURE ⭐⭐
( FISSURE - IN - ANO )
IAS - Internal anal sphincter
1) DEFINITION OF Anal fissure :-
Anal fissure is a small, superficial ulcer
present along the longitudinal axis of lower part of anal canal.
It can be present in the midline, posteriorly,
or anteriorly. Anterior ulcers are more
common in females.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
2) EXTERNAL ANAL SPHINCTER ANATOMY :-
Three parts :-
(a) Deep part - It encircles the upper end
of anal canal. There is no bony attachment.
(b) Superficial part - It is attached
posteriorly to coccyx & anteriorly to
mid perineal point in males & to vaginal
sphincter in females.
(c) Subcutaneous part - It encircles the
lower part of anal canal. There is no
bony attachment.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
3) INTERNAL ANAL SPHINCTER ANATOMY :-
It covers upper two third of anal canal. It
is formed by thickening of circular muscles which are continued from the bowel above. Spasm & contraction of sphincter causes fissure & other anal infections.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
4) CAUSES OF ANAL FISSURE :-
Anal fissure is caused due to tearing of anal canal due to trauma & ulcer formation at that place.
Following are the causes for trauma:-
(a) Hard stools - Can cause sphincter to
contract more forcefully leading to tear.
(b) Trauma
(c) Diarrhoea - Repeated diarrhoea
causes damage to anal mucosa.
(d) Sexually transmitted disease (STD)-
eg. syphilis , gonorrhoea (inflammation
& damage)
(e) Ischemia - Decrease in blood flow
delays healing & hastens tissue damage.
(f) Increased sphincter tone - It
decreases the blood supply to the anus
& thus slows down the healing process.
This can cause anal tear to develop.
(g) TB - inflammation & ulcer formation.
(h) Crohn's disease - inflammation &
ulcer formation.
(i) Ulcerative Colitis - inflammation &
ulcer formation.
(j) Anterior fissure is more common
in females than males because there
is weak support for the anterior anal
canal due to the presence of vagina
anterior to anus.
(k) haemorrhoidectomy - trauma during
surgical procedure.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
5) PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF ANAL
FISSURE :-
(a) The above causes may cause tear to
the anal mucosa leading to fissure.
(b) Due to fissure, the internal sphincter
remains contracted & doesn't relax
because damage to anal mucosa leads
to hypersensitivity of receptors in the
sphincter resulting in overreaction of the
continence reflex & hence the spasm of
sphincter occurs.
(c) Spasm of sphincter leads to decreased blood flow which further
delays healing of the fissure which can
transform the acute fissure into chronic
fissure.
(d) Pain occurs in fissure due to skin
damage, nerve damage & stimulation of
nociceptors present in damaged tissues.
This pain can be aggravated by ischemia
& infection.
The pain can also occur due to sphincter
spasm because spasm leads to
ischemia (leading to drop in pH &
release of pain producing substances
like bradykinin, ATP, H+ )
6) TYPES OF FISSURES :-
(a) Acute anal fissure - tear with clean &
sharp margins, no inflammation &
edema, severe pain , constipation &
spasm of sphincter.
(b) Chronic anal fissure -
# The margins are rolled out &
fibrosed.
# Inferior part of fissure has skin tag
which is edematous & guards the
fissure - sentinel pile. The upper part
shows hypertrophic papilla.
# Chronic fissure is inflammed &
edematous.
# There is less pain.
# It may undergo infection, abscess
formation, fibrosis or fistula formation.
# Multiple fissures - present in
homosexuals, Inflammatory Bowel
disease.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
7) CLINICAL FEATURES OF ANAL
FISSURE :-
(a) Pain (explained in pathophysiology)
# Severe in acute cases.
# Less severe in chronic cases - nerve
endings are in the process of healing.
(b) Bleeding, discharge - due to ruptured
blood vessels or due to abscess
formation.
(c) Constipation - due to pain & spasm.
(d) In case of acute fissure, Per rectal
examination or proctoscopy cannot be
done.(General anaesthesia is required)
(e) In case of chronic fissure, Per rectal
examination can be done & it can be felt
as BUTTON LIKE DEPRESSION with
enduration & sentinel pile.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
8) DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS :-
(a) Anal carcinoma.
(b) Anal chancre.
(c) TB of anus.
(d) Veneral diseases.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
9) TREATMENT OF ANAL FISSURE :-
(a) General measures :
# Drink plenty of water - so that stool
doesn't become hard.
# Fibre rich diet - soft stools.
# Stool softener - Lactulose.
Bulk forming agent - Psyllium.
# Application of local anaesthetic -
lignocaine, xylocaine.
# Sitz bath - increases blood flow &
relaxes muscles.
# Regular anal dilatation.
(b) Acute fissures :-
# Under general anaesthesia, dilatation
of anal sphincter is done by manual
stretching using two fingers of each
hand to relieve the spasm of
sphincter.
# Bed rest
# Application of local anaesthetic
(Xylocaine) or Nifedipine ointment
(causes relaxation of muscles -
Calcium Channel Blocker),
Laxatives.
(c) Chronic fissure :-
# Fissurectomy(excision of fissure) with Sphincterotomy (cutting open
of the sphincter & not complete
excision) - Sample is sent for ruling
out Carcinoma, TB.
# Botulinum toxin - It prevents the
release of Acetylcholine at
neuromuscular junction which causes
relaxation of sphincter.
# Nitroglycerin- GTN - It decreases the
tone of sphincter muscle by release of
nitrate which is converted into nitric
oxide which is a smooth muscle
relaxant.
# Diltiazem - Calcium Channel Blocker-
Smooth muscle relaxation.
# Regular anal dilatation.
# Lateral anal sphincterotomy - Internal
sphincter is divided away from the site
of fissure by open or close method.
CLOSE METHOD - Blade is inserted &
moved upwards in the intersphincteric
groove. (between external & internal
anal sphincter) Then, blade is moved
medially to cut the internal sphincter.
OPEN METHOD - Incision outside the
anal verge.(junction of perianal skin &
anal epithelium) - dissection of
hypertrophied internal sphincter & it's
division. Wound is left open.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐




Writing skill is very nice
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
Delete👍informative article
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteWell done Dr. Nikita😊
ReplyDeleteDoing very well beta✨
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
Delete👌👌
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteWow👌👌
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteTreatment part is best👍
ReplyDeleteबेटा, खुप सुंदर👌 खुप खुप आशीर्वाद
ReplyDeleteNice nice nice
ReplyDeleteलेखन शैली कौतुकास्पद👍
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
ReplyDeleteVery nice
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteGoood
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
Delete👌👌👌👌👌👌👌
ReplyDeleteThank you so much 😊😊
DeleteLiked all articles
ReplyDelete